Why is GAP Model useful in Service Marketing
GAP Model
The Gap Model is a useful framework in understanding the service
quality in in organization. First, lets know how is ‘service’ defined. American
Association of Marketing, AMA, defines ‘service’ as ‘activities, benefits, or
satisfaction that are offered for sale, or provided with connection with the sale
of goods’.
The Gaps Model was proposed by A Parasuraman, Valaris Zeithaml
and LL Bery in 1985 in the Journal of Marketing.The major factors for determining the Gap Model are as
follows:
- ·
Customer Expectation
- ·
Customer Perception of Service
- ·
Management perception of customer expectation
- ·
Customer Driven Service Designs and Standards
- ·
Service Delivery
- ·
External Communication to Customers
These are the various touchpoints in the customer journey
that determine which gap is prevalent in the service provided.
 |
There are two types of Gaps: Gap in the Customer side and gap
in the Company side.
CUSTOMER GAP
Difference between
expectation and perception
Also known as the Listening Gap
Customer Gap exists in the mind of customers. It occurs when
there is mismatch between the Expected Service and Perceived Service. The customer
might get the real quality service but if it is different from what the customer
had ‘expected’, it leads to Customer Gap. Even if the service provided is of
quality bit the customer does not ‘perceive’ it as a quality then this also leads
to Customer Gap.
Key Factors leading to Customer Gap:
i.
Customers are unaware of actual service provided
ii.
Miscommunication
iii.
Over-expectation of service
PROVIDER
GAP
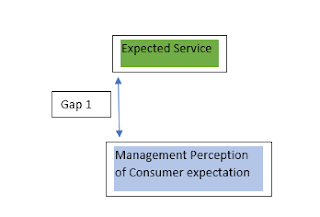
1. Provider
Gap 1: Knowledge Gap
Not knowing
what customers want
i.
Inadequate Marketing Research Orientation
·
Insufficient marketing research
·
Marketing research not focused on service quality
ii.
Lack Of Upward Communication
·
Lack of interaction between management and customers
·
Too many layers between contact personnel and top
management
iii.
Insufficient Relationship Focus
·
Focus on transaction rather than relationships
·
Focus on new customers rather than relationship
customers
iv.
Inadequate Service Recovery
·
Lack of encouragement to listen to customer complaints
·
No appropriate recovery mechanisms in place for service
failures
2. Provider
Gap2: Standard Gap
Not selecting
the right service design and standards
i.
Poor Service Design
·
Unsystematic new service development process
·
Vague, undefined service designs
ii.
Absence Of Customer-Driven Standards
·
Lack of customer-driven standards
·
Absence of formal process for setting service quality
goals
iii.
Inappropriate Physical Evidence And Services Cape
·
Failure to develop tangibles inline with customer
expectation
·
Inadequate maintenance and updating of the service
scape
3. Provider
Gap 3: Delivery Gap
Not delivering
to service standards
i.
Deficiencies In Human Resource Policies
·
Ineffective recruitment
·
Role ambiguity and role conflict
·
Inappropriate evaluation and compensation systems
ii.
Failure To Match Supply And Demand
·
Over-reliance on price to smooth demand
·
Inappropriate customer mix
iii.
Customers Not Fulfilling Roles
·
Customers lack knowledge of their roles and
responsibilities
·
Customers negatively impact each other
iv.
Problems With Service Intermediaries
·
Channel conflict over objectives and performance
·
Channel conflict over costs and rewards
·
Tension between empowerment and control
·
Difficulty controlling quality and consistency
4. Provider
Gap 4: Communication Gap
Not matching
performance to promises
i.
Lack Of Integrated Service Marketing Communication
·
Not including interactive marketing in communications
plan
·
Absence of strong internal marketing program
ii.
Ineffective Management Of Customer Expectation
·
Not adequately educating customers
·
Not managing customer expectation through all forms of
communication
iii.
Overpromising
·
Overpromising in advertising
·
Overpromising in personal selling
·
Overpromising through physical evidence cues
iv.
Inadequate Horizontal Communications
·
Inadequate communications between sales and operations
·
Inadequate communications between advertising and operations
·
Difference in policies across branches
CLOSING THE
GAPS
i.
Use research, complaint analysis, customer panels
iii.
Improve upward communications
iv.
Act on insights and information
2. Closing GAP 2: Establish the right Service Quality
Standards
i.
Top management should be commited to providing service
quality
ii.
Establish challenging and realistic service quality
goals
iii.
Train mangers to be service quality leaders
iv.
Be receptive to new ways to deliver service quality
v.
Set, communicate and reinforce customer-oriented
service standards
vi.
Measure performance of service standards and provide regular
feedbacks
vii.
Reward managers and employees for achievement of
quality goals
3. Closing GAP 3: Ensure that service performance meets
standards
i.
Attract the best employees
ii.
Select the right employees
iii.
Develop ad support employees
iv.
Retain good employees
4. Closing GAP 4: Ensure that service delivery matches promise
i.
Seek input from operations personnel on what can be
done
ii.
Reality in advertising
iii.
Better communications between sales, operations and
marketing
iv.
Internal marketing programs
v.
In advertising, focus on service characteristics that
are important to customers
vi.
Manage Customer expectations



Wow it is really wonderful and awesome thus it is very much useful for me to understand many concepts and helped me a lot.
ReplyDeleteComplete SAS Training & Certification Course in Noida, India
Best Tally Training Center in Noida with Certified Institute
I admire this article for the well-researched content and excellent wording. I got so involved in this material that I couldn’t stop reading. I am impressed with your work and skill. Thank you so much
ReplyDeleteDigital Marketing Course Under 15000 with 35 Module
Advanced Excel Training is important & Where to learn