HYPOTHESIS Testing
 |
| Source: https://www.sixsigma-institute.org |
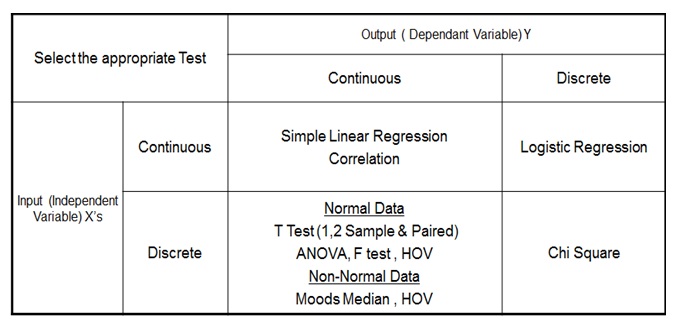
Here, we will discuss the several types of Hypothesis testing for Discrete Independent variables.
1.
T Test
T-Test is used to determine the hypothesis for cases. The t test is one type of
inferential statistics. It is used to determine whether there is a significant
difference between the means of two groups. With all inferential statistics, we
assume the dependent variable fits a normal distribution.
A t test is used when we wish to compare two means (the
scores must be measured on an interval or ratio measurement scale.)
Following assumptions are made for T-test
·
The samples have been randomly drawn from their
respective populations
·
The scores in the population are normally
distributed
·
The scores in the populations have the same
variance (s1=s2)
T test is appropriate when there is only one independent
variable and one dependent variable.
1.
Simple T-test
Simple T-Test is used in cases when there
are two levels within the independent variable. For example: the impact of
training employees on the efficiency of their performance. The research
question for t-test would be “Is there significant impact of training on the
efficiency of employees?”
2.
Independent T-Test
Independent T-test is used when there are
more than two levels in the independent variable. For example: “Is there
significant impact of training on the efficiency of lower management, middle management
and top management on their work efficiceny?”
3.
Paired T-Test
Paired T-test is used in cases where there
is a pre and a post analysis. The same research/survey is conducted on the same
set of population before and after an event. For example: “Efficiency of
employees before and after the week long training.”
2.
ANOVA
ANOVA is short for ANalysis Of Variance. ANOVA is used when
there are more than two levels of Independent variables and only one dependent
variable. For example: “impact of Surf excel, Rin and Wheel on the cleanliness
of the cloth.” ANOVA can be said to be combination of n number of T-test.
ANOVA can have two or more independent variables too. A
two-way ANOVA has two independent variables. And it has three research
questions: One for each of the two independent variables and one for the
interaction of the two independent variables.
Sample Research Questions for a Two-Way ANOVA:
Do
Democrats, Republicans, and Independents differ on their opinion about a tax
cut?
Do males and
females differ on their opinion about a tax cut?
Is there an interaction between gender and political party
affiliation regarding opinions about a tax cut?
3.
MANOVA
MANOVA is short for Multiple ANalysis Of Variance. MANOVA is
best used when there are multiple independent variables and multiple dependent
variables. MANOVA is a combination of n number of ANOVA.
MANOVA is complicated and it is advised to use ANOVA n times
rather than using MANOVA.
References:
https://researchbasics.education.uconn.edu/t-test
https://researchbasics.education.uconn.edu/anova_regression_and_chi-square

Comments
Post a Comment